Code Completion
Go Up to Getting Started with RAD Studio
Code Completion (Ctrl+Space) is a Code Insight feature available in the Code Editor, which makes completing your code easy.
Code Completion displays a resizable "hint" window that lists valid elements that you can select to add to your code. The hint window shows a list where the first symbols are the ones that start with the text you type, followed by the symbols that contain the rest of the text.
Also, you can control the sorting of items in the Code Completion hint window by right-clicking the box and choosing Sort by Name or Sort by Scope.
Different items appear in different colors and various formats in the Code Completion list. For example, by default:
- Keywords are dark blue.
- Procedure, function, and property names are black and boldfaced.
- When filtering, the matching characters are drawn underlined. (This can be turned off).
Contents
Invoking Code Completion
Automatic code completion is on by default, and options for enabling and disabling Code Completion are located on the Tools > Options > Editor > Language and click on Code Insight option.
- When Auto Invoke is enabled for Code Completion, typing a period (.) and an opening parenthesis (i.e., starting a method call) invokes Code Completion for both Delphi and C++.
- You can always use
Ctrl+Spaceto invoke Code Completion in Delphi and C++ even if the Auto Invoke option is disabled on Code Insight Options. - If the Delay option is set on Code Insight Options, a delay timer runs (the cursor spins) before Code Completion is invoked.
Code Completion for C++ on macOS Requires Initial Compile: Code Completion requires that you have compiled at least once your C++ desktop project for the macOS target platform. Before compiling the project, ensure that your environment meets all requirements, as described in Setting Up Your Development Environment for macOS.
When you compile the project, RAD Studio creates the precompiled header file (such as
myProject.pch) in theC:\Users\<user>\Documents\Embarcadero\Studio\Projects\OSX32folder. If you erroneously deleted theprojectname.pchfile, Code Completion is unavailable for your project until you compile the project again.
Code Completion Window
This section illustrates the Code Completion window for a small code block. Let's say you have a collection of buttons.
var
GViewButtons: TObjectList<TToolButton>;
In your application, you need to do a for loop through the buttons in the collection, and you do not know how many buttons are in the collection. Your code block is similar to the following:
begin
{ ... }
if Assigned(GViewButtons) then
for I := 0 to GViewButtons. - 1 do
begin
{ something }
end;
{ ... }
end;
Move your cursor beyond the . (period character) after the GViewButtons statement, and press Ctrl+Space. The Code Completion window appears, as follows:
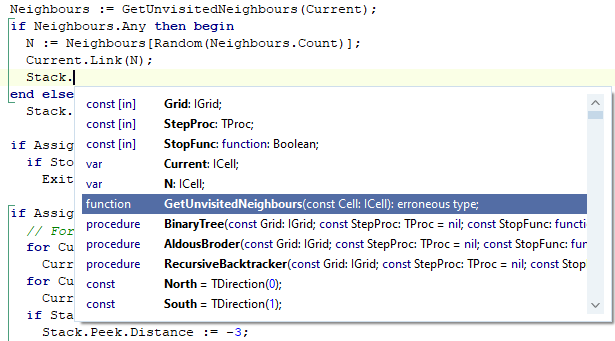
Locate the Count property and hit ENTER or TAB. Your code will be completed to:
begin
{ ... }
if Assigned(GViewButtons) then
for I := 0 to GViewButtons.Count - 1 do
begin
{ something }
end;
{ ... }
end;
As of RAD Studio 12.0, the footer section of the Code Completion window contains symbols that you can apply depending on how you invoke the completion.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
|
Acceptance keys |
Indicates keys that accept and insert the currently selected item in the completion list. |
|
List navigation |
Indicates keys that can be used to change selection in the completion list, the up and down arrow icons. |
|
Cancellation |
Indicates keys that will close the completion list without inserting any code. |
Using Code Completion
The following are specific ways to use Code Completion in the IDE:
- To display the properties, methods, and events available in a class, press
Ctrl+Spaceafter the name of a variable that represents either a class instance or a pointer to a class instance. If Auto Invoke is on, it will automatically appear as you type. - To invoke code completion for a pointer type, the pointer must first be dereferenced. For instance:
- In C++, type:
this-> - In Delphi, type:
Self.
- In C++, type:
- Type an arrow (->) for a pointer to an object.
- You can also type the name of non-pointer types followed by a period (.) to see the list of inherited and virtual properties, methods, and events. For instance:
- In C++ type:
TRect test;test. - In Delphi, type:
var test: TRect; begin test.
- In C++ type:
- Type an assignment operator or the beginning of an assignment statement, and press
Ctrl+Spaceto display a list of possible values for the variable. - You can code completion units or files for the uses clause Delphi or #include statements C++. Note that the provided list currently may not include all files or units you expect:
- In Delphi, inside a uses clause, add a comma after the last unit and press
Ctrl+Space. You can type to filter the units. - In C++, type "#include<" and press
Ctrl+Space; a list of known headers will be shown. You can type to filter the headers.
- In Delphi, inside a uses clause, add a comma after the last unit and press
- In C++, type the scope operator (
::). - Type a procedure, function, or method call and press
Ctrl+Spaceto display a list of arguments that are valid for assignment to the variable entered. Select a list item followed by an ellipsis (...) to open a second list of related arguments compatible with the variable entered in the assignment statement. - Type a record (in Delphi) or a structure (in C++) to display a list of fields.
- Type an array property (not a genuine array), and press
Ctrl+Spaceto display an index expression. - In C++, you can also press
Ctrl+Spaceon a blank statement line to display symbols from additional RTL units even if they are not used by the current unit. - In Delphi, the reserved words appear in the Code Completion window if you have enabled Show reserved words on the Tools > Options > Editor > Language > Code Insight dialog box. The words that appear are determined by the context when you invoke Code Completion. The current list of Delphi reserved words is available in the Delphi Language Guide (Fundamental Syntactic Elements).
Canceling Code Completion or Dismissing the Code Completion Window
- To dismiss the Code Completion window, press the
Esckey or click outside the window.
Browsing to a Declaration
When the Code Completion window is displayed, you can hold down Ctrl and click any identifier in the list to browse to its declaration.
Also, if you hover the mouse pointer over the identifier in the Code Editor, a hint window tells where the identifier is declared. You can press Ctrl, point to the identifier in the code (it changes to blue underline, by default, and the insertion point changes to a hand pointing), and then click (with the mouse) to move to its declaration.
When using the C++ Classic Compiler, Code Completion features work best when you have already built your application and have created a precompiled header. Otherwise, you need to wait for the compiler to generate the required information. It is recommended that you set the PCH Usage option on the Project > Options > C++ Compiler Precompiled Headers dialog box. Choose "Generate and use".
When using the C++ Clang Compiler, the Code Insight feature compiles each C++ file stand alone. It does not use the precompiled header PCH. Code completion requires a well-formed C++ code that includes what it uses. If a unit does not include all headers it relies on, instead of relying on the PCH causing them to be indirectly included, Code Insight will fail to parse the unit and will not provide results for code completion.
To solve the issues, review the Error Insight results starting from the very top of the file. According to the errors, you can include a file if requested or improve your C++ code.Code Keywords
Code Completion includes language keywords in the completion list.
Keep in mind that Keywords are auto-selected ahead of identifiers. This means that even when code completion automatically invokes whatever you type, as long as it is valid, it completes correctly.
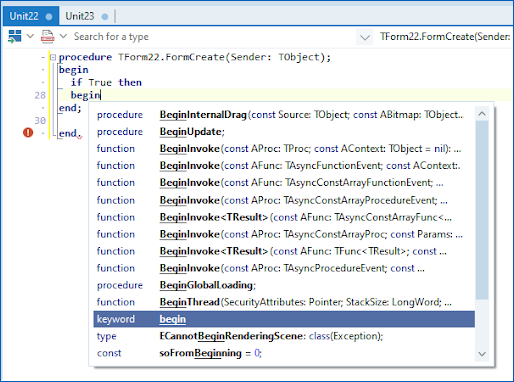
You can turn off keywords (reserved words) being included in the completion list. If you do this, we recommend you to turn off completion auto-invoke too, changing it to Only on dot.
Code Templates
Code templates can be configured to display only in specific unit areas, such as in a type declaration.
- memberdecl: TFoo = class | end;
- methoddecl: procedure | or function |
- decl: var | or const |
- typedecl: type |
- methodbody: begin | end;