Resolving Name Duplication in Parent and Child Entities (Unification)
Go Up to Working with Relationships
Contents
The Duplicate Attribute Editor displays when you create or rename primary key attributes, relationships, or foreign keys and it duplicates existing attributes, columns, or foreign keys in child tables or entities. For example, if you have two entities called Parent and Child where Parent has a primary key called Key and Child also has an attribute called Key, when you create a relationship from Parent to Child, then the Duplicate Native Attribute Editor launches where you must decide how to handle the propagated attributes.
- If the child entity has a foreign key with the same name as the parent entity, the Duplicate Attribute Editor launches if you have selected Prompt to Resolve FK Columns on the Application tab of the Options editor. Choose Tools > Options.
- The option, Allow Unification when Editing Names on the Options Editor - Name Handling tab allows you to change the role names of foreign attribute or columns to the same names as other attributes or columns in the same Entity or Table.
The following will help you understand how to use the Duplicate Attribute Editor :
Attribute Name Editing Options
The following describes the options and functionality on the Duplicate Attribute Editor :
- Propagating Attributes to Resolve : Displays a list of the Attributes/Columns that are duplicates. Select the propagating attribute that you want to resolve then select the way you want to propagate.
- Replace Native Attribute with propagating Attribute : If selected, ER Studio Data Architect replaces the attribute in the child with the propagated foreign key attribute. If the relationship is deleted from the main model, ER Studio Data Architect removes the propagated attribute and original native attribute from the child entity.
- Rolename propagating Attribute : If selected, you can rename the foreign key so that the native attribute in the child entity can still exist with its original name. After propagation, both attributes will exist in the child entity.
- Change Native Attribute Name to allow propagating Attribute Name : If selected, you can rename the original native attribute in the child entity so that the attribute name from the parent entity can be used for the foreign key. After propagation, both attributes will exist in the child entity.
- Unify Native Attribute with propagating Attribute : If selected, ER Studio Data Architect unifies the propagating foreign with the native attribute in the child table. If the relationship is later deleted, ER Studio Data Architect leaves the native child attribute.
Examples of Duplicate Name Resolutions
The following examples illustrate how duplicate names are resolved depending on the options chosen in the Duplicate Attribute Editor dialog.
- Replace Native Attribute with Propagating Attribute
- Rolename Propagating Attribute
- Change Native Attribute Name to Allow Propagating Attribute Name
- Unify Native Attribute with Propagating Attribute
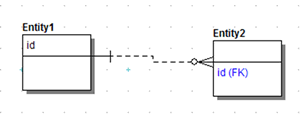
Replace Native Attribute with Propagating Attribute
If selected, ER Studio Data Architect replaces the attribute in the child with the propagated foreign key attribute. If the relationship is deleted from the main model, ER Studio Data Architect removes the propagated attribute and original native attribute from the child entity.
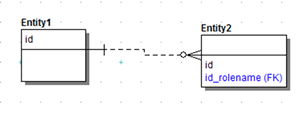
Rolename Propagating Attribute
If selected, you can rename the foreign key so that the native attribute in the child entity can still exist with its original name. After propagation, both attributes will exist in the child entity.
- To resolve the naming conflict, in the Duplication Attribute Editor you can specify the rolename idrolename for the foreign key.
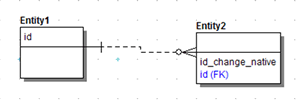
Change Native Attribute Name to Allow Propagating Attribute Name
If selected, you can rename the original native attribute in the child entity so that the attribute name from the parent entity can be used for the foreign key.
- To resolve the foreign key, the new child name is specified as id_change_native.
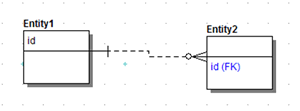
Unify Native Attribute with Propagating Attribute
If selected, ER Studio Data Architect unifies the propagating foreign with the native attribute in the child table.
- ER Studio Data Architect keeps id in the child entity if you delete the relationship.