DataSnap REST
Go Up to Developing DataSnap Applications
Representational State Transfer (REST) is the client-server architecture used by the World Wide Web. Conforming to REST constraints is referred to as being RESTful. A RESTful web service is implemented using HTTP (hypertext transfer protocol) and the principles of REST.
Contents
Topics
- Request Filters
- JavaScript REST Proxy
- DBX Parameter Caching
- REST Heavyweight Callbacks
- REST Client Library
- Authentication with a JavaScript Client
- JavaScript client Sessions
- DataSnap REST Messaging Protocol
DataSnap REST Overview
The REST protocol assumes that the server is able to serve four types of requests: GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE. These operations represent Retrieve, Update, Insert, and Delete data operations. These operations are assimilated with the server methods through a mapping protocol. REST assumes that each server method can be invoked as one of the operations above through a dispatch mechanism that assumes a mapping between the URI (Uniform Resource Identifier) path, method name, and parameters.
URI Mapping
The server responds to URIs. The general HTTP request has the following format:
http://my.site.com/datasnap/rest/URIClassName/URIMethodName[/inputParameter]*
The content is accepted by POST and PUT requests, assimilated with Update and Put requests. The default protocol maps the URI to various server methods depending on the command type.
| Command type | Mapping pattern | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
|
URICclassName.URIMethodName |
Utility.Storage |
|
|
URIClassName.acceptURIMethodName |
Utility.acceptStorage |
|
|
URIClassName.updateURIMethodName |
Utility.updateStorage |
|
|
URIClassName.cancelURIMethodName |
Utility.cancelStorage |
Depending on the command type, a request such as http://my.site.com/datasnap/rest/utility/storage can be mapped to one of the four methods above, depending on the command type. It is assumed that a method mapped through a GET request returns the object, or a collection of objects based on the input parameters.
For example, a server method called Utility.Storage(Key: String): TJSONValue; matches the GET command:
http://my.site.com/datasnap/rest/utility/storage/test.
A POST request will invoke Utility.UpdateStorage(Key: String; Data: TJSONValue);. The request content is mapped to the input parameter data, the URI postfix is mapped to the key.
A PUT request will invoke Utility.AcceptStorage(Key: String; Data: TJSONValue);. The method is assumed to insert into the storage area the data parameter under the key provided. The request content is mapped to the second input parameter.
Finally, a DELETE request will invoke Utility.CancelStorage(Key: String); that is supposed to remove the object from the storage area with the given key.
The mapping pattern can be overridden. The user can override the mapping for each type based on class name and method name parameters.
Customizing the URL for REST Requests
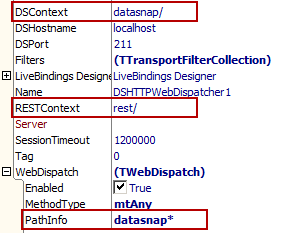
You can easily customize parts of the URL for a REST request. You can change the standard DataSnap context from datasnap/ to mycontext/, for instance. Also, you can change the REST context from rest/ to myrest/, for instance. To do this:
- Switch to the WebModule of your DataSnap REST server application.
- Select the TDSHTTPWebDispatcher component.
- In the Object Inspector, locate the DSContext property.
- Change from datasnap/ to mycontext/ (or whatever you require). Remember to add the closing /.
- In the Object Inspector, locate the WebDispatch property and expand it.
- Update the PathInfo subproperty from datasnap* to mycontext*.
- In the Object Inspector, locate the RESTContext property.
- Change from rest/ to myrest/ (or whatever you require). Remember to add the closing /.
These changes will cause the DataSnap server to process requests that begin with
/mycontext/myrest
instead of
/datasnap/rest
Additionally, some changes are needed so that clients will use the correct URL. These changes imply updating the js\connection.js file. You have to update setConnection to:
function setConnection(host, port, urlPath)
{
connectionInfo = {"host":host,"port":port,"authentication":null,"pathPrefix":urlPath};
connectionInfo.dscontext = 'mycontext';
connectionInfo.restcontext = 'myrest';
}
Response Numbers
Depending on the URI, exposed methods, execution results, the following codes are returned:
| Code | Reason | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
404 |
Datasnap keyword is missing from URI |
http://my.site.com/rest |
|
501 |
REST (or other protocol) keyword is missing |
http://my.site.com/datasnap/x/y/z |
|
501 |
Command type unrecognized |
Other commands than |
|
200 |
Execution successful |
The response contains the output parameters {"result":[parameterValue[,parameterValue]*]} |
|
201 |
|
The response contains the output parameters {"result":[parameterValue[,parameterValue]*]} |
|
500 |
Method execution failed, reason incorporated in the response |
- |
Exposing a Server Method
Once the server class is registered with the DataSnap Server, any method should be HTTP callable if the signature allows it. If no user-defined mapping is provided, the server methods need to match the name convention above in order to be available for HTTP REST requests.
The parameters are mapped from the URI immediately after the server method name. If the number of parameters does not match or they are not input or input/output parameters, an error is returned.
See Also
- REST Client Library
- DataSnap REST Application Wizard
- Connecting the Client to DataSnap Server
- RESTful Web Services
- Building Web Services the REST Way
Samples
- REST Surf Spot Finder sample (Delphi)
- REST Surf Spot Finder sample (C++)