Creating and Deploying a classes.dex File Manually
Go Up to Using a Custom Set of Java Libraries In Your RAD Studio Android Apps
Creating and deploying a classes.dex file manually allows you not only to add libraries to your application, but also to modify the built-in RAD Studio Java libraries for Android, or remove those that you do not need. If you just need to add a custom Java library to your application for Android, see Adding A Java Library to Your Application Using the Project Manager.
Contents
Creating a classes.dex File
The classes.dex file is a Dalvik Executable file that all Android applications must have. This file contains the Java libraries that the application uses.
When you deploy an application for Android, RAD Studio includes a classes.dex file that contains the RAD Studio built-in Java libraries. To use your own Java libraries in your RAD Studio applications, you must create a new classes.dex file that includes both those RAD Studio built-in Java libraries that your application needs and your own Java libraries.
Determining Which JAR Files to Include in Your classes.dex File
To create your new classes.dex file, you need the JAR files of every Java library that your applications use, as well as the JAR files of the libraries on which those libraries depend.
This affects the RAD Studio built-in Java libraries as well. For example, if your applications need the Google Play Services Java library, your classes.dex file must also contain the JAR file of the Google Play Application Licensing Java library, because Google Play Application Licensing is a dependency of Google Play Services. If Google Play Application Licensing had its own dependencies, you would have to include those as well.
The following table lists the dependencies of the RAD Studio built-in Java libraries:
| Library | JAR File | Dependencies | Required by RAD Studio |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Yes | ||
|
|
|
Yes | |
|
|
No | ||
|
|
No | ||
|
|
No | ||
|
|
|
No | |
|
|
|
No | |
|
|
|
No | |
|
|
|
No |
You can find these JAR files in the following folders within the RAD Studio installation folder (C:\Program Files (x86)\Embarcadero\Studio\23.0):
lib\android\debuglib\android\release
You can either include all the RAD Studio built-in Java libraries in your classes.dex file or determine, based on the information in the table above, which RAD Studio built-in Java libraries your applications need.
- Warning: You must always include the Java libraries that are Required by RAD Studio in your custom
classes.dexfile.
Generating a classes.dex File from JAR Files
Once you have determined which JAR files your Android applications need, you can create a classes.dex file from them.
To create a classes.dex file, you need to use the command-line tool dx. You can find this command-line tool at C:\Users\Public\Documents\Embarcadero\Studio\23.0\CatalogRepository\AndroidSDK-<Version>.
Run dx with the --dex parameter, the --output parameter with the output path of the classes.dex file as its argument, and a space-separated list of paths to the JAR files that you want to include in the generated classes.dex file. For example:
dx --dex --output="classes.dex" "C:\Path\To\Library1.jar" "C:\Path\To\Library2.jar"- Note: You should create both a debug and a release version of your
classes.dexfile. The RAD Studio debugging features are only available if the deployedclasses.dexfile contains the debug versions of the included RAD Studio built-in Java libraries.
Deploying the classes.dex File
- Warning: Follow these steps carefully. Android applications must always include a valid
classes.dexfile. For more information, see Invalid or Missingclasses.dexFile below.
To configure your Android application to be deployed with your custom classes.dex file:
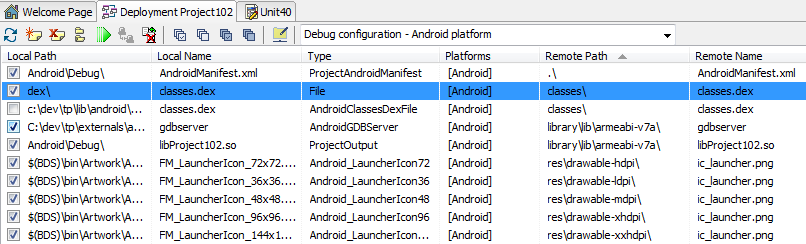
- Select Project > Deployment to open the Deployment Manager.
- Uncheck the checkbox of the default
classes.dexfile. - Click the
 button and add your custom
button and add your custom classes.dexfile to the list of deployment files. - Change the Remote Path of your new entry to
classes\. - Change the Platforms of your new entry to Android only.
Troubleshooting
Invalid or Missing classes.dex File
This is the error message that you see when you run an application on an Android device using RAD Studio and your application does not have a valid classes.dex file:
Unable to create process: Unable to install '<APK file>'. Failure [INSTALL_FAILED_DEXOPT]
An Android application package (APK file) must always contain a valid classes.dex file. That is:
- There must be a
classes.dexfile in the APK file. - The
classes.dexfile must be located atclasses/classes.dexwithin the APK file. - The
classes.dexmust be a valid Dalvik executable.
When you use a custom classes.dex file, you must be careful. After you unckeck the default classes.dex file on the Deployment Manager and you add an entry for your custom classes.dex file:
- Make sure that the entry of your custom file is checked.
- Make sure that the Remote Path of your new entry is
classes\. - Make sure that your new entry is your
classes.dexfile, and not a different file that may not be a valid Dalvik executable.
If your Android application is not configured to be deployed with a valid classes.dex file, and you run your application on an Android device from RAD Studio or install on your device an APK file of your application generated with RAD Studio, the installation will fail, but it will leave data in your Android device preventing you from installing applications with the same package name as your application (see Android Version Info).
After you attempt to install an APK file without a valid classes.dex file, the only know solution is to perform a factory reset of your Android device.
- Warning: A factory reset removed all date from your device (personal data, custom settings, and more). Carefully consider whether fixing the issue is worth losing your data. If you decide to go forward, remember to back up your data before you perform the factory reset.