InterBase Quick Start: Part II - Creating Indexes
Go Up to InterBase Quick Start: Part II - Data Definition
An index is based on one or more columns in a table. An index orders the contents of the specified columns and stores that information on disk in order to speed up access to those columns. Although indexes improve the performance of data retrievals, thay also take up disk space and can slow inserts and updates. That is why indexes are typically used on frequently queried columns. Indexes can also enforce uniqueness and referential integrity constraints.
InterBase automatically generates indexes on UNIQUE and PRIMARY KEY columns. See the Data Definition Guide for more information about constraints.
You use the CREATE INDEX statement to create an index. The simplified syntax is:
CREATE INDEX index_name
ON table (columns)
Optionally, you can add one or more of the ASCENDING, DESCENDING, or UNIQUE keywords following the CREATE INDEX keywords.
Contents
 Creating the Name Index
Creating the Name Index
Define the following index for the Employee table:
CREATE INDEX namex
ON Employee (last_name, first_name)
This statement defines an index called namex for the last_name and first_name columns in the Employee table.
By default indices reside in the same tablespace as that of the table unless a different tablespace is specified. For more information on table spaces refer to the Tablespace documentation.
Preventing Duplicate Index Entries
To define an index that eliminates duplicate entries, include the UNIQUE keyword in CREATE INDEX. When you define a UNIQUE index, users cannot insert or update values in indexed columns if the same values already exist.
For unique indexes defined on multiple columns, such as prodtypex in the example below, the same value can be entered within individual columns, but the combination of values entered in all columns of the index must be unique for each row.
You cannot create a NIQUE index on columns that already contain non-unique values.
 Creating a UNIQUE Index
Creating a UNIQUE Index
Create a unique index named prodtypex, on the Project table:
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX prodtypex
ON Project (product, proj_name)
Specifying Index Sort Order
By default, SQL stores an index in ascending order. To make a descending sort on a column or group of columns more efficient, use the DESCENDING keyword to define the index.
 Creating a DESCENDING Index
Creating a DESCENDING Index
Enter and execute the following code to create an index called budgetx that is ordered in a descending order:
CREATE DESCENDING INDEX budgetx
ON Department (budget)
Modifying Indexes
To change an index definition you must first drop the index and then create a new index.
 Altering the Name Index
Altering the Name Index
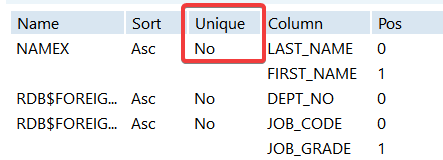
First examine the current definition of the namex index.
- The
namexindex was created on theEmployee tableso select that table in the left pane of IBConsole. - Right-click the Employee table and select Properties.
- Choose Show Indexes on the Menu bar of the Properties window (
 ).
).
- You can see that the
Namexindex is notUNIQUE. - Enter and execute the following
DROP INDEXstatement:DROP INDEX namex
- Enter and execute the following to redefine the
Namexindex so that it includes theUNIQUEkeyword:CREATE UNIQUE INDEX namex ON Employee (last_name, first_name)
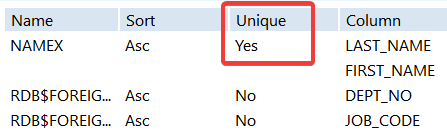
- Once again, open the Properties window for the
Employee tableand choose Show Indexes. - You can see that now the
Namexindex isUNIQUE.
 Assigning indexes to a tablespace
Assigning indexes to a tablespace
This section shows how to assign an Index to a tablespace. Use the ALTER INDEX clause to assign existing indices to a tablespace.
Note:By default all indices belong to the Primary tablespace. In the context of InterBase tablespaces when you assign an index to a tablespace you move it from the Primary to another existing tablespace.
ALTER INDEX {<tablespace_name> | PRIMARY}
[ALTER TABLESPACE {<tablespace_name> | PRIMARY}]
First use ALTER INDEX to modify the NAMEX index, then use ALTER TABLESPACE to move the NAMEX index to the employee_tblspc tablespace.
ALTER INDEX NAMEX
ALTER TABLESPACE employee_tblspc
 Removing indexes from a tablespace
Removing indexes from a tablespace
This section shows how to remove an index from a tablespace.
In the context of InterBase tablespaces, when you remove an index from a tablespace you move it to the
Primary or to another existing tablespace.ALTER INDEX {<tablespace_name> | PRIMARY}
[ALTER TABLESPACE {<tablespace_name> | PRIMARY}]
First use ALTER INDEX to modify the NAMEX index, then use ALTER TABLESPACE to move the NAMEX index to the Primary or another existing tablespace.
ALTER INDEX NAMEX
ALTER TABLESPACE primary
Time to Back up
Once you succesfully complete this part of the tutorial, it is a good time to back up your database.