InterBase Quick Start: Part IV - Grouping and Ordering Query Results
From InterBase
Go Up to InterBase Quick Start: Part IV - Retrieving Data
A database does not store rows in any particular order. When you execute a query, you can see that the result is not organized in any way. The ORDER BY clause lets you specify how to organize the result. You can use the GROUP BY clause to group the results of aggregate functions.
Ordering Query Results
The syntax of the ORDER BY clause is:
ORDER BY [col_name | col_num] [ASC | DESC] [[col_name | col_num] [ASC | DESC], …]
The statement lets you specify more than one column. You can refer to columns by column name or by column position (an integer).
By default, InterBase uses ASCENDING order. If you want the order to be DESCENDING, you have to specify it.
 Using ORDER BY
Using ORDER BY
- Execute the following query:
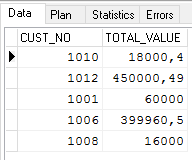
SELECT cust_no, total_value FROM Sales WHERE total_value > 10000
You can see that the result in not ordered:
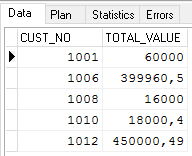
- Modify the previous query to order the results by the
cust_nocolumn:SELECT cust_no, total_value FROM Sales WHERE total_value > 10000 ORDER BY cust_no
Now the result shows the
cust_nocolumn in ascending order: - Order the result set by the total value of the sales, in descending order:
SELECT cust_no, total_value FROM Sales WHERE total_value > 10000 ORDER BY total_value DESC
- To see the effect of ordering by more than one column, execute the following query:
SELECT last_name, first_name, phone_ext FROM Employee ORDER BY last_name DESC,first_name