InterBase Quick Start: Part IV - Using the GROUP BY Clause
From InterBase
Go Up to InterBase Quick Start: Part IV - Grouping and Ordering Query Results
You use the optional GROUP BY clause to organize data that you retrieve from aggregate functions. When you issue a query that has both aggregate (AVG, COUNT, MIN, MAX, or SUM) and non-aggregate columns, you must use GROUP BY to group the result set by each of the non-aggregate columns. The following rules apply:
- Each column from which you are doing a non-aggregate
SELECTmust appear in theGROUP BYclause. - The
GROUP BYclause can reference only columns that appear in theSELECTclause. - Each
SELECTclause in a query can have only oneGROUP BYclause.
The definition of a group is: a subset of rows that match a distinct value in the columns of the GROUP BY clause.
 Grouping the Result Set of Aggregate Functions
Grouping the Result Set of Aggregate Functions
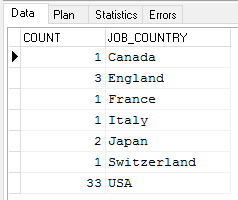
Execute the following query to find out how many employees there are in each country:
SELECT COUNT(emp_no),
job_country
FROM Employee
GROUP BY job_country
The result set looks like this: