InterBase Quick Start: Part IV - Using the WHERE Clause
From InterBase
Go Up to InterBase Quick Start: Part IV - Retrieving Data
The WHERE clause follows the SELECT and FROM clauses. It must precede the ORDER BY clause. The WHERE clause tests data to see whether it meets certain conditions, so that the SELECT statement returns only the rows that meet the WHERE condition. The WHERE clause allows you to precisely specify which data you want to retrieve.
 Using WHERE
Using WHERE
- Enter the following statement to return only rows in which
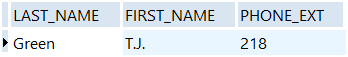
Greenis the value of thelast_namecolumn.SELECT last_name, first_name, phone_ext FROM Employee WHERE last_name = 'Green'
The query returns one row:
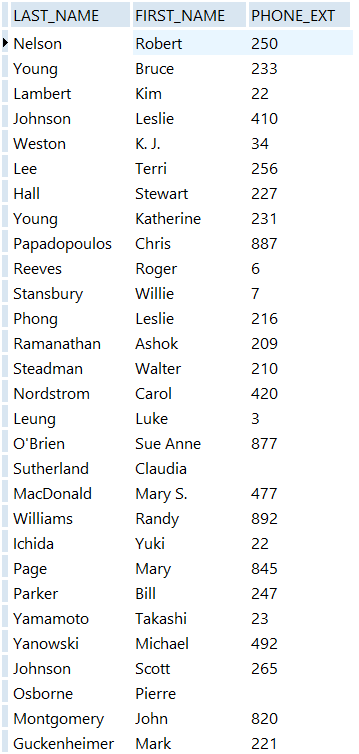
- Now modify the previous query: change the equal sign to a greater than sign. The result includes all the rows in which the last name is alphabetically greater than
Green.SELECT last_name, first_name, phone_ext FROM Employee WHERE last_name > 'Green'
The query returns 29 rows:
Topics
- Search Conditions
- Pattern Matching
- Testing for an Unknown Value
- Comparing Against a Range or List of Values
- Logical Operators
- Controlling the Order of Evaluation